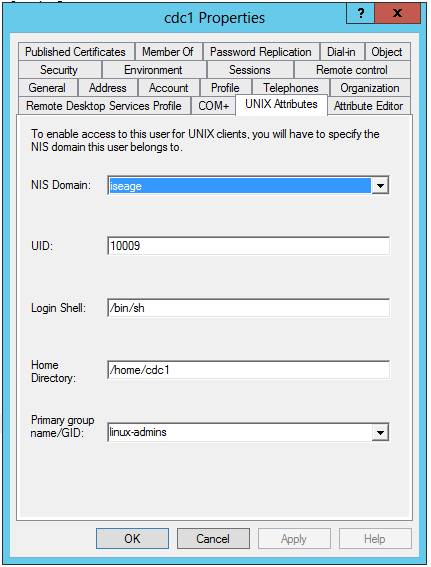
Using the LDAP plugin available for PAM, it’s possible to do LDAP authentication without joining the domain. Note however that this requires installing Identity Management for Unix on your domain controllers. See this tutorial for more information.
Before we proceed, it’s a good idea to take a snapshot. I’ll wait for you to do that.
Once that’s done, install the required packages:
pkg install nss_ldap openldap-client pam_ldap pam_mkhomedir (FreeBSD 10)
--or--
pkg_add -r nss_ldap openldap-client pam_ldap pam_mkhomedir (FreeBSD 9 and earlier)
These packages are going to require some configuration. First, edit /usr/local/etc/openldap/ldap.conf – all you should need to change are the BASE and URI lines:
# LDAP Defaults
#
# See ldap.conf(5) for details
# This file should be world readable but not world writable.
BASE dc=teamN,dc=isucdc,dc=com
URI ldap://ad.teamN.isucdc.com
#SIZELIMIT 12
#TIMELIMIT 15
#DEREF never
The next bit is long but most of it will be commented out. You’ll need to edit /usr/local/etc/ldap.conf and /usr/local/etc/nss_ldap.conf. These files should be exactly identical – you can either copy one to the other or symlink one to the other; I’ll leave that up to you. Feel free to copy the entirety of the following. Alternatively, just modify the italicized lines.
Note: this assumes that the user account you made for ldap queries is named “ldap” – substitute whatever you named the account.
# This is the configuration file for the LDAP nameservice
# switch library and the LDAP PAM module.
#
# PADL Software
# http://www.padl.com
#
# Your LDAP server. Must be resolvable without using LDAP.
# Multiple hosts may be specified, each separated by a
# space. How long nss_ldap takes to failover depends on
# whether your LDAP client library supports configurable
# network or connect timeouts (see bind_timelimit).
#Don't use this, use the uri line instead
#host ad.teamN.isucdc.com
# The distinguished name of the search base.
base dc=teamN,dc=isucdc,dc=com
# Another way to specify your LDAP server is to provide an
# uri with the server name. This allows to use
# Unix Domain Sockets to connect to a local LDAP Server.
uri ldap://ad.teamN.isucdc.com
#uri ldaps://127.0.0.1/
#uri ldapi://%2fvar%2frun%2fldapi_sock/
# Note: %2f encodes the '/' used as directory separator
# The LDAP version to use (defaults to 3
# if supported by client library)
ldap_version 3
# The distinguished name to bind to the server with.
# Optional: default is to bind anonymously.
binddn ldap@teamN.isucdc.com
# The credentials to bind with.
# Optional: default is no credential.
bindpw ldap_user's_password
# The distinguished name to bind to the server with
# if the effective user ID is root. Password is
# stored in /etc/ldap.secret (mode 600)
#rootbinddn cn=manager,dc=padl,dc=com
# The port.
# Optional: default is 389.
#port 389
# The search scope.
scope sub
#scope one
#scope base
# Search timelimit
#timelimit 30
# Bind/connect timelimit
#bind_timelimit 30
# Reconnect policy: hard (default) will retry connecting to
# the software with exponential backoff, soft will fail
# immediately.
bind_policy soft
# Idle timelimit; client will close connections
# (nss_ldap only) if the server has not been contacted
# for the number of seconds specified below.
#idle_timelimit 3600
# Filter to AND with uid=%s
#pam_filter objectclass=account
# The user ID attribute (defaults to uid)
#pam_login_attribute uid
# Search the root DSE for the password policy (works
# with Netscape Directory Server)
#pam_lookup_policy yes
# Check the 'host' attribute for access control
# Default is no; if set to yes, and user has no
# value for the host attribute, and pam_ldap is
# configured for account management (authorization)
# then the user will not be allowed to login.
#pam_check_host_attr yes
# Check the 'authorizedService' attribute for access
# control
# Default is no; if set to yes, and the user has no
# value for the authorizedService attribute, and
# pam_ldap is configured for account management
# (authorization) then the user will not be allowed
# to login.
#pam_check_service_attr yes
# Group to enforce membership of
#pam_groupdn cn=PAM,ou=Groups,dc=padl,dc=com
# Group member attribute
#pam_member_attribute uniquemember
# Specify a minium or maximum UID number allowed
#pam_min_uid 0
#pam_max_uid 0
# Template login attribute, default template user
# (can be overriden by value of former attribute
# in user's entry)
#pam_login_attribute userPrincipalName
#pam_template_login_attribute uid
#pam_template_login nobody
# HEADS UP: the pam_crypt, pam_nds_passwd,
# and pam_ad_passwd options are no
# longer supported.
#
# Do not hash the password at all; presume
# the directory server will do it, if
# necessary. This is the default.
#pam_password clear
# Hash password locally; required for University of
# Michigan LDAP server, and works with Netscape
# Directory Server if you're using the UNIX-Crypt
# hash mechanism and not using the NT Synchronization
# service.
#pam_password crypt
# Remove old password first, then update in
# cleartext. Necessary for use with Novell
# Directory Services (NDS)
#pam_password clear_remove_old
#pam_password nds
# RACF is an alias for the above. For use with
# IBM RACF
#pam_password racf
# Update Active Directory password, by
# creating Unicode password and updating
# unicodePwd attribute.
#pam_password ad
# Use the OpenLDAP password change
# extended operation to update the password.
#pam_password exop
# Redirect users to a URL or somesuch on password
# changes.
#pam_password_prohibit_message Please visit http://internal to change your password.
# RFC2307bis naming contexts
# Syntax:
# nss_base_XXX base?scope?filter
# where scope is {base,one,sub}
# and filter is a filter to be &'d with the
# default filter.
# You can omit the suffix eg:
# nss_base_passwd ou=People,
# to append the default base DN but this
# may incur a small performance impact.
#nss_base_passwd ou=People,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_shadow ou=People,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_group ou=Group,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_hosts ou=Hosts,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_services ou=Services,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_networks ou=Networks,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_protocols ou=Protocols,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_rpc ou=Rpc,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_ethers ou=Ethers,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_netmasks ou=Networks,dc=padl,dc=com?ne
#nss_base_bootparams ou=Ethers,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_aliases ou=Aliases,dc=padl,dc=com?one
#nss_base_netgroup ou=Netgroup,dc=padl,dc=com?one
# attribute/objectclass mapping
# Syntax:
#nss_map_attribute rfc2307attribute mapped_attribute
#nss_map_objectclass rfc2307objectclass mapped_objectclass
# configure --enable-nds is no longer supported.
# NDS mappings
#nss_map_attribute uniqueMember member
# Services for UNIX 3.5 mappings
#nss_map_objectclass posixAccount User
#nss_map_objectclass shadowAccount User
#nss_map_attribute uid msSFU30Name
#nss_map_attribute uniqueMember msSFU30PosixMember
#nss_map_attribute userPassword msSFU30Password
#nss_map_attribute homeDirectory msSFU30HomeDirectory
#nss_map_attribute homeDirectory msSFUHomeDirectory
#nss_map_objectclass posixGroup Group
#pam_login_attribute msSFU30Name
#pam_filter objectclass=User
#pam_password ad
# configure --enable-mssfu-schema is no longer supported.
# Services for UNIX 2.0 mappings
#nss_map_objectclass posixAccount User
#nss_map_objectclass shadowAccount user
#nss_map_attribute uid msSFUName
#nss_map_attribute uniqueMember posixMember
#nss_map_attribute userPassword msSFUPassword
#nss_map_attribute homeDirectory msSFUHomeDirectory
#nss_map_attribute shadowLastChange pwdLastSet
#nss_map_objectclass posixGroup Group
#nss_map_attribute cn msSFUName
#pam_login_attribute msSFUName
#pam_filter objectclass=User
#pam_password ad
# RFC 2307 (AD) mappings
nss_map_objectclass posixAccount user
nss_map_objectclass shadowAccount user
nss_map_attribute uid sAMAccountName
nss_map_attribute homeDirectory unixHomeDirectory
nss_map_attribute shadowLastChange pwdLastSet
nss_map_objectclass posixGroup group
nss_map_attribute uniqueMember member
pam_login_attribute sAMAccountName
pam_filter objectclass=User
pam_password ad
#Uncomment the following line to override the default login shell
nss_override_attribute_value loginShell /usr/local/bin/bash
# configure --enable-authpassword is no longer supported
# AuthPassword mappings
#nss_map_attribute userPassword authPassword
# AIX SecureWay mappings
#nss_map_objectclass posixAccount aixAccount
#nss_base_passwd ou=aixaccount,?one
#nss_map_attribute uid userName
#nss_map_attribute gidNumber gid
#nss_map_attribute uidNumber uid
#nss_map_attribute userPassword passwordChar
#nss_map_objectclass posixGroup aixAccessGroup
#nss_base_group ou=aixgroup,?one
#nss_map_attribute cn groupName
#nss_map_attribute uniqueMember member
#pam_login_attribute userName
#pam_filter objectclass=aixAccount
#pam_password clear
# Netscape SDK LDAPS
#ssl on
# Netscape SDK SSL options
#sslpath /etc/ssl/certs
# OpenLDAP SSL mechanism
# start_tls mechanism uses the normal LDAP port, LDAPS typically 636
#ssl start_tls
#ssl on
# OpenLDAP SSL options
# Require and verify server certificate (yes/no)
# Default is to use libldap's default behavior, which can be configured in
# /etc/openldap/ldap.conf using the TLS_REQCERT setting. The default for
# OpenLDAP 2.0 and earlier is "no", for 2.1 and later is "yes".
#tls_checkpeer yes
# CA certificates for server certificate verification
# At least one of these are required if tls_checkpeer is "yes"
#tls_cacertfile /etc/ssl/ca.cert
#tls_cacertdir /etc/ssl/certs
# Seed the PRNG if /dev/urandom is not provided
#tls_randfile /var/run/egd-pool
# SSL cipher suite
# See man ciphers for syntax
#tls_ciphers TLSv1
# Client certificate and key
# Use these, if your server requires client authentication.
#tls_cert
#tls_key
# Disable SASL security layers. This is needed for AD.
#sasl_secprops maxssf=0
# Override the default Kerberos ticket cache location.
#krb5_ccname FILE:/etc/.ldapcache
# SASL mechanism for PAM authentication - use is experimental
# at present and does not support password policy control
#pam_sasl_mech DIGEST-MD5
Whew! We’re getting there, next step is to modify /etc/nsswitch.conf – modify the group and passwd lines to include the “ldap” option:
#
# nsswitch.conf(5) - name service switch configuration file
# $FreeBSD: release/10.0.0/etc/nsswitch.conf 224765 2011-08-10 20:52:02Z dougb $
#
group: cache files ldap
group_compat: nis
hosts: files dns
networks: files
passwd: cache files ldap
passwd_compat: nis
shells: files
services: compat
services_compat: nis
protocols: files
rpc: files
Alright, now comes the hairy bit: PAM configuration. Pay close attention here – incorrect PAM configuration could permanently lock you out of your system! If you haven’t already, TAKE A SNAPSHOT NOW.
Alright, we’re on the home stretch now! Edit /etc/pam.d/sshd – this affects how users log in over SSH:
#
# $FreeBSD: release/10.0.0/etc/pam.d/sshd 197769 2009-10-05 09:28:54Z des $
#
# PAM configuration for the "sshd" service
#
# auth
auth sufficient pam_opie.so no_warn no_fake_prompts
auth sufficient /usr/local/lib/pam_ldap.so no_warn
auth requisite pam_opieaccess.so no_warn allow_local
#auth sufficient pam_krb5.so no_warn try_first_pass
#auth sufficient pam_ssh.so no_warn try_first_pass
auth required pam_unix.so no_warn try_first_pass
# account
account required pam_nologin.so
#account required pam_krb5.so
account required pam_login_access.so
account required /usr/local/lib/pam_ldap.so no_warn ignore_authinfo_unavail ignore_unknown_user
account required pam_unix.so
# session
#session optional pam_ssh.so want_agent
session required /usr/local/lib/pam_mkhomedir.so umask=0077
session required pam_permit.so
# password
#password sufficient pam_krb5.so no_warn try_first_pass
password required pam_unix.so no_warn try_first_pass
Note carefully the placement and exact syntax of the added lines (the pam_ldap.so and pam_mkhomedir.so bits). pam_mkhomedir will automatically make home directories for users that exist in LDAP but have never logged in. The umask sets permissions on these directories – 0077 corresponds to running “chmod 700 /home/username”. For a more relaxed setting, try 0022 instead – this will allow users to read from, but not write to, other users’s home directories by default.
Alright, that’s all the config files! Let’s test this out by restarting sshd:
service sshd restart
--or--
/etc/rc.d/sshd restart
Try logging in as a user you set up UNIX attributes for in Active Directory. This almost certainly isn’t going to work the first time – carefully go over the AD configuration and all the config files above before proceeding. If you’ve accidentally completely locked yourself out of SSH, you can still get in via the console – comment out the lines you added in /etc/pam.d/sshd and restart sshd again to regain access.
Once you’ve gotten everything working, reboot the box. Make sure everything still works and that you can log in. If you’re completely satisfied, you can also CAREFULLY edit /etc/pam.d/system – this file deals with logins to the console. This is optional and should only be attempted if you plan on logging in to the console with an AD account. If you’re unsure, don’t edit this file as an error in it will permanently lock you out of console logins!
#
# $FreeBSD: release/10.0.0/etc/pam.d/system 197769 2009-10-05 09:28:54Z des $
#
# System-wide defaults
#
# auth
auth sufficient pam_opie.so no_warn no_fake_prompts
auth sufficient /usr/local/lib/pam_ldap.so no_warn
auth requisite pam_opieaccess.so no_warn allow_local
#auth sufficient pam_krb5.so no_warn try_first_pass
#auth sufficient pam_ssh.so no_warn try_first_pass
auth required pam_unix.so no_warn try_first_pass nullok
# account
#account required pam_krb5.so
account required pam_login_access.so
account required /usr/local/lib/pam_ldap.so no_warn ignore_authinfo_unavail ignore_unknown_user
account required pam_unix.so
# session
#session optional pam_ssh.so want_agent
session required /usr/local/lib/pam_mkhomedir.so umask=0022
session required pam_lastlog.so no_fail
# password
#password sufficient pam_krb5.so no_warn try_first_pass
password required pam_unix.so no_warn try_first_pass